MBPX
Alfa Laval MBPX is a range of pharma centrifuges with high bowl speeds specially for microbiological applications. They are well suited to the separation of suspended solids with particle sizes of approx. 0.5 to 500 μm. The range incudes small lab machines as well as large scale production ones. They come in two versions: a traditional top entry open, non-hermetic version or a hollow-spindle fully hermetic version.
Designed for minimal shear stress, absence of oxygen, low power consumption and low noise level
- Minimal product loss and downstream processing costs thanks to adjustable discharge volume which ensures solids with high dry matter content
- High separation capacity due to bowl geometry
- Designed for easy CIP
- All product-wetted polymers and seal rings compliant with FDA or USP Class IV regulations
- FDA compliant materials in mechanical seals
Complete, skid-mounted separation system
An MBPX 810 separation system consists of a stainless steel skid with the disk-stack separator and all the auxiliary equipment required for safe and efficient operation.
The system is factory tested and ready for operation after connection to the process stream flows and electrical supply.
Non-hermetic or fully hermetic versions
The MBPX is available in two versions depending on process requirements - a traditional top entry open, non-hermetic version or a hollow spindle, fully hermetic version.
The MBPX non-hermetic version
The MBPX non-hermetic separation system features a substantial solids collection space and a variable discharge size that gives great flexibility in handling a wide range of biomass loadings. Furthermore, it incorporates Alfa Laval's patented disc inlet that regardless of flow rate minimises shear in the acceleration zone, thereby improving separation performance as protein flocs or microbial cells will not be damaged.
The MBPX fully hermetic version
The MBPX fully hermetic separation system combines easy installation with superb separation performance. The hermetic design is achieved by a combination of a hollow-spindle inlet, a hermetic outlet and a separator bowl completely filled with liquid. The unique hermetic hollow-spindle inlet ensures the gentlest acceleration of particles, preventing them from lysing. It is ideal for mammalian cell cultures. The hermetic in- and outlet design also completely avoids air entrainment and other related problems with oxidization and foam.
A complete range
Non-hermetic range
- MBPX 404S separation system for laboratory and pilot scale production with capacities ranging from 100 l/h to 300 l/h
- MBPX 507S separation system for pilot and small scale production with capacities ranging from 400 l/h to 800 l/h
- MBPX 810S separation system for medium scale production with capacities ranging from 1,200 l/h to 2,500l/h
Fully hermetic range
- MBPX 810H separation system for medium scale production with capacities ranging from 1,500 l/h to 3,000 l/h
- MBPX 714H separation system for large scale production with capacities ranging from 3,000 l/h to 8,000 l/h
- MB 601H separation system for large scale production with capacities ranging from 3,500 l/h to 10,000 l/h
- MB 701H separation system for large scale production with capacities ranging from 5,000 l/h to 12,000 l/h
How it works
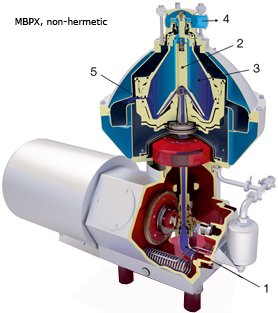
MBPX, non-hermetic version
The feed enters the centrifuge bowl from the top via a stationary inlet pipe (1) and is accelerated by the disc inlet (2) in the distributor before entering the disc stack (3), where the separation takes place between the discs.
The separated liquid phase leaves through the liquid outlet at the top of the bowl (4). The heavier solids phase is collected at the periphery of the bowl from where it is discharged via solids ports (5) at pre-set intervals.
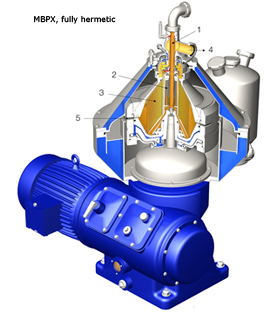
MBPX, fully hermetic version
The feed enters the rotating centrifuge bowl from the bottom via a hollow spindle inlet (1) and gradually accelerates in a distributor (2) as it enters the disc stack (3), where the separation takes place between the discs.
The separated liquid phase leaves through the liquid outlet at the top of the bowl 4). The heavier solids phase is collected at the periphery of the bowl from where it is discharged via the solids ports (5) at pre-set intervals.

